Written by Tambiama Madiega with Rafał Ilnicki.
Economic indicators show that the United States (US) is the front-runner for both private investment in artificial intelligence (AI) and venture capital in generative AI, followed by China. US companies are also developing most of the large languages models (LLMs) underpinning AI innovation. EU starts-up are beginning to scale up.
Investment in AI and generative AI

The global AI market was valued at over €130 billion* in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially by 2030, up to nearly €1.9 trillion (Statista, 2023). Private investment now accounts for most of the investment in AI. The US is leading private investment in AI (€44 billion) in 2022, followed by China (€12 billion) (Figure 1). The EU and the United Kingdom (UK) together attracted €10.2 billion worth of private investment in 2022 (Stanford University, 2023).
Between 2018 and the third quarter of 2023, almost €32.5 billion was invested in EU AI companies, compared with more than €120 billion in US AI companies. Recent investments in US AI companies (e.g. OpenAI and Anthropic) have widened the gap between the EU’s and the US’s relative share of private investment in AI (Atomico, 2023). Public investment in AI is growing as well. The EU Digital Europe programme will fund AI with a total of €2.1 billion in the 2021‑2027 period.
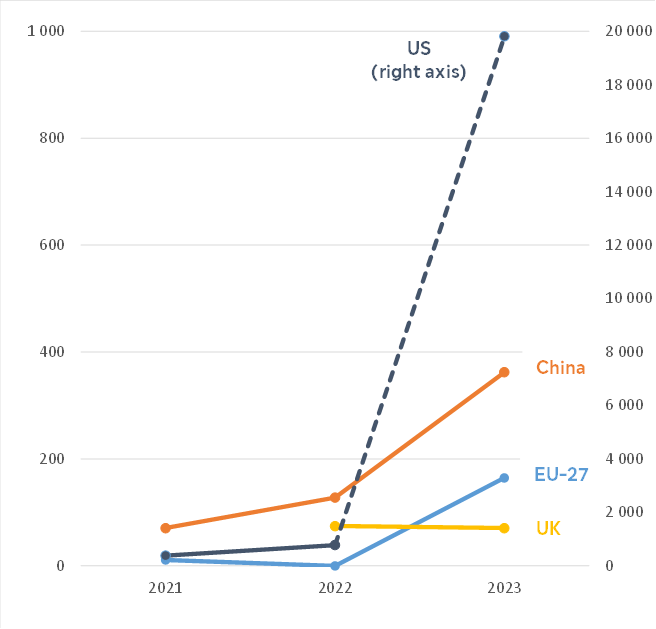
Generative AI technology allows for the generation of new content (e.g. text, video) and enables faster product development. Generative AI tools are making a significant impact across all industry sectors and helping to shape new products and services, for instance in the health (e.g. medicines), high-tech (e.g. media content) and banking (e.g. data analytics) sectors (McKinsey, 2023). The US is the clear leader in generative AI venture capital investment** (see Figure 2). US companies raised some €7.4 billion for generative AI between 2020 and 2022 (McKinsey, 2023). This investment grew significantly between 2022 and 2023 (OECD/Preqin, 2024) and now accounts for more than half of all AI investment in the US (Atomico, 2023).
* An exchange rate of 0.93 USD/EUR was applied when the original currency was USD.
** Venture capital is a form of private equity and a type of financing that investors offer to start-up companies and small businesses.
Examples of generative AI start-ups and LLMs
Generative AI is powered by general-purpose AI (GPAI) models and LLMs, i.e. deep-learning algorithms trained on large datasets to create new content, services and products. Companies worldwide are investing in generative AI (Table 1). Investment in generative AI concerns three segments: infrastructure, applications and models. Model makers raised over 70 % of generative AI private funding in the 2019-2023 period. This investment is required to sustain the high cost of LLM training and deployment (Dealroom, 2023).
| Country | Company | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Mistral AI | IT infrastructure and hosting |
| Contents | Media, social platforms, marketing | |
| Aleph Alpha | IT infrastructure and hosting | |
| China | MiniMax | IT infrastructure and hosting |
| Emotibot Technology | IT infrastructure and hosting | |
| Brilliant Labs Limited | Consumer products | |
| US | OpenAI | Media, social platforms, marketing |
| Primer Technologies | Government, security and defence | |
| Anthropic | IT infrastructure and hosting | |
| UK | Google DeepMind | Education and training |
| Stability AI | Business processes and support services | |
| AutogenAI | Media, social platforms, marketing |
In January 2024, the EU introduced measures to support European start-ups and small and medium-sized enterprises in developing trustworthy AI by granting access to funding, including the Horizon Europe, Digital Europe, EIC accelerator and InvestEU programmes. Moreover, the Regulation on establishing the European high-performance computing joint undertaking (EuroHPC Regulation) is being amended, so that EU companies can access AI supercomputers to train LLMs.
Recent research shows that 73 % of LLMs are being developed in the US and another 15 % in China, while EU companies are struggling to release this kind of technology (Table 2). The choice between developing closed models (where the models’ source code is proprietary) or open-source models (freely and publicly accessible for anyone to modify, study, build on, and use) has significant consequences, including in terms of market concentration, transparency and security risks. The EU’s AI Act lays down specific rules for GPAI models. All providers of GPAI models (except for free and open source models) must meet transparency requirements and respect EU copyright rules when training their models. Moreover, GPAI models trained using a total computing power of more than 1025 FLOPs (floating-point operations per second) will be presumed to carry systemic risks. When confirmed by the Commission’s investigations, providers of these models will be required to assess and mitigate those risks continuously and ensure an adequate level of cybersecurity protection. So far only GPT4 and a few other models seem to be close to the 1025 FLOPs threshold.
| Company | Example of product | Headquarters | Open source or proprietary |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI21labs | Jurassic-2 | Israel | Proprietary |
| Aleph Alpha | Luminous | Germany | Open source |
| Alibaba | Qwen-7B | China | Open source |
| Anthrop\c | Claude 2 | US | Proprietary |
| Cohere | Cohere Command | Canada, US | Proprietary |
| Gemini | US | Proprietary | |
| Meta | LLaMA 2-70B | US | Open source |
| Mistral AI | Mistral 7B | France | Open source |
| OpenAI | GPT-4 | US | Proprietary |
| Tencent | Hunyuan | China | Proprietary |
Read this ‘at a glance’ note on ‘AI investment: EU and global indicators‘ in the Think Tank pages of the European Parliament.




Comments are closed for this post.